CO2 Ventilation Assessment
Overview
This project uses CO2 monitors as tracer gas instruments to assess indoor ventilation rates and air quality. Better ventilation means healthier indoor spaces.
Why CO2?
Since most indoor CO2 comes from human exhalation, measuring CO2 levels tells us how much of the air we're breathing has been exhaled by others - the "rebreathe fraction." This is directly relevant to airborne disease transmission.
- Outdoor CO2: ~420 ppm
- Well-ventilated indoor: under 800 ppm
- Poorly ventilated: 1000+ ppm
The Tracer Gas Method
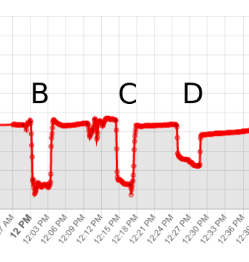
Beyond simple monitoring, CO2 can be used as a "tracer gas" to measure air changes per hour (ACH):
- Inject a known amount of CO2 into a room
- Monitor the decay rate as ventilation replaces the air
- Calculate ACH from the decay curve
This gives a quantitative measure of ventilation quality.
Practical Applications
- Assessing classroom ventilation
- Evaluating workspace air quality
- Testing the effectiveness of ventilation improvements
- Informing decisions about air purifier placement
To find out more, visit: Edge Collective - CO2 Ventilation